The National Institute of Digestive Diseases describes hemorrhoids as swollen and inflamed veins around the anus or in the lower rectum, which affect 3 out of 4 adults during their lifetime. Causes are generally from events that put extra pressure in the lower rectum like straining during a bowel movement, prolonged sitting or heavy lifting. Sometimes a patient has none of these risk factors and the cause of their hemorrhoids is unknown. Common symptoms are bleeding, feeling of fullness in rectum, itching/pain around the anus and protruding lumps from the anus.
Since hemorrhoids are so common, I wanted to go over a few basics regarding potential options for treatment hemorrhoids and when I would recommend seeing a doctor.
What are Internal and External Hemorrhoids?
There are two types of hemorrhoids – internal and external. In order to properly describe both, I first need to describe an area of anatomy (rectum and anus). The rectum is the last part of the large intestine leading to the anus. The anus is the opening at the end of the digestive tract where bowel contents leave the body. It’s important to understand that distinction when describing the two types of hemorrhoids.
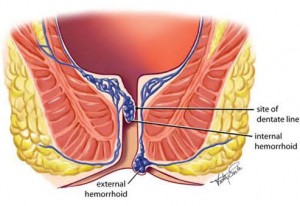 External hemorrhoids are under the skin around your anus and you can feel them on the outside. Sometimes blood may clot in an external hemorrhoid, which forms a lump near your anus. When irritated, external hemorrhoids can itch or bleed.
External hemorrhoids are under the skin around your anus and you can feel them on the outside. Sometimes blood may clot in an external hemorrhoid, which forms a lump near your anus. When irritated, external hemorrhoids can itch or bleed.
Internal hemorrhoids are located inside the rectum. They are usually painless and often go undetected. Sometimes they get big enough they pop in and out of the anus. When pressure irritates the surface of the hemorrhoid bleeding can occur.
When to see a Doctor for Hemorrhoids?
Common symptoms of hemorrhoids can be an indicator of more serious health issues, so it is important to be evaluated by a physician to rule out any serious issues. In my San Antonio gastroenterology practice, I often see patients experiencing rectal bleeding or blood in the toilet. Since this is the most prevalent symptom for hemorrhoids, I wanted to start by saying that while it can be very alarming to see blood in the toilet it is generally easy to treat. That being said, all bleeding is abnormal and you should always see a doctor if you experience any bleeding.
Other than rectal bleeding, I recommend seeing your doctor if you experience any of the following:
- Moderate rectal pain that lasts longer than 1 week
- A lump inside the anus that increases in size or becomes painfulness
- Stool that changes in either size, shape or color
How are Hemorrhoids Diagnosed and Treated?
If you are having problems that you think may be hemorrhoid related, see your physician. Diagnosing hemorrhoids is easy and painless. And don’t feel embarrassed, hemorrhoids are very common and we look at a lot of butts. Your physician will examine your anus and rectum and may use a small anoscope (clear plastic device a little bigger around than a finger) that allows them to look up into your anus at the hemorrhoid veins. Once this exam is done we can determine if they are internal hemorrhoids, external hemorrhoids or both
Treatment for internal vs external hemorrhoids is a bit different. External hemorrhoids are usually treated with topical medication, fiber and fluids to avoid straining during bowel movements, soaking in warm bath (Sitz bath), and if all this fails then surgical removal. External hemorrhoids cannot be “banded” as they are covered by skin which has pain sensors and would be too painful. Internal hemorrhoids are treated similar to external hemorrhoids, but we have the advantage of being able to band them as well. Since internal hemorrhoids are not covered by pain sensors we can place rubber band on them to shrink them down and usually avoid the need for surgical removal. For more details on rubber band ligation, please visit my hemorrhoid banding page.
External Hemorrhoid Treatments
- Ice packs
- Suppositories
- Creams
- Warm Sitz bath
- Surgical treatments
Internal Hemorrhoid Treatments
- Rubber band ligation
- Suppositories
- Topical creams
- Surgery




